What is GATE ?
The Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE) is an all -India Examination conducted by the six Indian Institutes of Technology and Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, on behalf of the National Coordinating Board - GATE, Ministry of Human Resources Development (MHRD), Government of India.From Freshersworld point of view we have tried our best to give you a clear picture of GATE.
Objective
To identify meritorious and motivated candidates for admission to Post Graduate Programmes in Engineering, Technology, Architecture and Pharmacy at the National level. To serve as benchmark for normalisation of the Undergraduate Engineering Education in the country.
To identify meritorious and motivated candidates for admission to Post Graduate Programmes in Engineering, Technology, Architecture and Pharmacy at the National level. To serve as benchmark for normalisation of the Undergraduate Engineering Education in the country.
Here is an opportunity for advanced engineering education in India. An M.E or M.Tech degree is a desirable qualification for our young engineers seeking a rewarding professional career. Engineering students, while in the final year of their degree course, spend considerable time in seeking an opening for studies in foreign universities.
Structure of GATE Examination
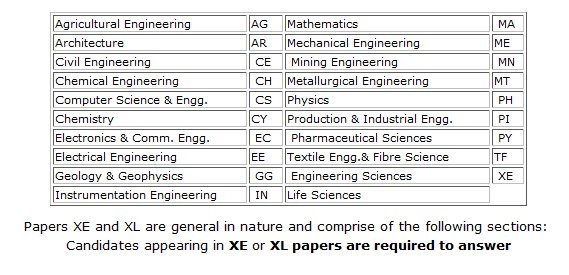
The GATE exam held every year on the second Sunday of February, across the country in over 100 cities. At present nearly 60,000 students write GATE every year. Candidates can choose a single paper of 3 hours duration to appear in GATE from the discipline papers shown in the following Table.In Three Sections, one compulsory as indicated below:
GateSyllabus | |
PAPER CODE | PAPER NAME |
AG | Agricultural Engineering |
AR | Architecture and Planning |
CE | Civil Engineering |
| CH | Chemical Engineering |
| CS | Computer Science & Engineering |
| CY | Chemistry |
| EC | Electronics & Comm Engineering |
| EE | Electrical Engineering |
| GG | Geology & Geophysics |
| IN | Instrumentation Engineering |
| IT | Information Technology |
| MA | Mathematics |
| ME | Mechanical Engineering |
| MN | Mining Engineering |
| MT | Metallurgical Engineering |
| PH | Physics |
| PI | Production & Industrial Engg. |
| PY | Pharmaceutical Sciences |
| TF | Textile Engg. & Fiber Science |
| XE | Engineering Sciences |
| XL | Life Sciences |
GATE Tips:
1.Material Collection
- Syllabus
- All the relevant books based on the subject(Divide the books in two groups - (1) Fundamental and basic concepts (2) Problem oriented
- Some books helpful for pre-requisite knowledge on the subject
- Some good guide books for GATE
- Previous questions papers
3.Study - Syllabus and Previous questions papers
4.Start from the first chapter
- read at least 5 books, it will widen your knowledge(if necessary consult with the books for pre-requisite knowledge or with some expert)
- Note down the probable concepts(definitions, unit, dimension etc.)
- Note down necessary theories, formulae etc
- Solve problems as maximum as possible(from text books, Guide books etc)
- Think about various tricks in solving problems(if necessary, note it)
- Go for series of self tests based on this chapter(take other's help to conduct tests)
- Continue the self tests until getting a very good score
7.Finally, go for self tests based on whole syllabus(take other's help to conduct these tests)
8.On the exam day…you will be at the Pick, who can stop you?
GATE Results
The GATE result is declared every year on 31 st March and the score of the qualified candidates shows their All India Rank and Percentile Score in the discipline paper chosen by the candidates.
GATE Score Card
-
Score card will be sent only to the qualified candidates. No information will be sent to candidates who are not qualified. -
The GATE score card is a valuable document. Care should be taken to preserve it. Additional Score Cards, (upto a maximum of two) will be issued on payment basis only once. -
The Score Card cannot be treated as a proof of category. -
The score card of the Qualified Candidates will include GATE Score, Percentile Score and Rank.
i. GATE Score
The GATE SCORE of a candidate is a statistical performance index in the range 0 to 1000. It reflects the ability of a candidate, irrespective of the paper or year in which he/she has qualified. Candidates with same GATE SCORE from different disciplines and/or years can be considered to be of equal ability.
m = marks obtained by the candidate.
a = average of marks of all candidates who appeared in the paper mentioned on this scorecard, in the current year.
s = standard deviation of marks of all candidates who appeared in the paper mentioned on this scorecard, in the current year.
K1 and K2 are determined respectively from the mean and standard deviation of marks of all candidates across all papers and years since GATE 2002.
A typical qualitative interpretation of the GATE SCORE, for example, can be as follows:
The percentile score is not the same as percentage of marks. The percentile score of a candidate shows what percentage of candidates, who appeared in the same paper in GATE 2005, scored less marks than him/her. It is calculated as follows: Let N be the total number of candidates appearing in that paper and nc be the number of candidates who have the same all India rank c in the same paper (there can be bunching at a given all India rank). Then all the candidates, whose all India rank is r, will have the same percentile score P, where
The percentile score in each paper is calculated as follows: Let N be the total number of candidates appearing in that paper, and nc be the number of candidates who have the same all India rank c in the same paper (there can be bunching at a given all India rank), then all the candidates, whose all India rank is r, will have the same percentile score P, where
P = {(no. of candidates securing marks less than the candidate concerned)/N}x100
-
The evaluation of the ORS is carried out by a computerized process using scanning machines, with utmost care. Requests for revaluation of the answer script and re-totaling of marks will not be entertained. -
The GATE result and particulars of the qualified candidates will be made available to interested organizations (educational institutions, R and D laboratories, industries etc.) in India and abroad based on written request by the organization and on payment. Details can be obtained from GATE Chairmen of IITs / IISc.
Are you the right one to apply for ?
The following categories of candidates are eligible to appear in GATE:
-
Bachelor's degree holders in Engineering/Technology/Architecture/Pharmacy and those who are in the final or pre-final year of such programmes. -
Master's degree holders in any branch of Science/Mathematics/Statistics/Computer Applications or equivalent and those who are in the final or pre-final year of such programmes.
-
Candidates in the second or higher year of the Four-year Integrated Master's degree programme (Post-B.Sc.) in Engineering/Technology or in the third or higher year of Five-year Integrated Master's degree programme and Dual Degree programme in Engineering/ Technology. -
Candidates with qualifications obtained through examination conducted by professional societies recognised by UPSC/AICTE as equivalent to B.E./B.Tech. Those who have completed Section A or equivalent of such professional courses are also eligible.
GATE Pattern:
The pattern of GATE examination has been CHANGED from 2005.
-
Main PapersThe question paper will be fully objective type for a total of 150 marks divided into three groups:-
Group I: Question Numbers 1 to 30 (30 questions) will carry one mark each. -
Group II: Question numbers 31 to 80 (50 questions) will carry two marks each. -
Group III: Question Numbers 81a to 85b (10 questions) will carry two marks each. Each number in this series (81,82,83,84,85) will have two sub-questions (a & b). The answer to part 'b' will be linked to the correct answer to part 'a', as described below in Section (e)(vi).
-
Each question will have four choices for the answer. Only one choice is correct.
Wrong answers carry 25% negative marks in Q1 to Q80 and Q81a, 82a, 83a, 84a and 85a. Marks for correct answers to Q81b, 82b, 83b, 84b and 85b will be given only if the answer to the corresponding part 'a' is correct. However, Q81b, 82b, 83b, 84b and 85b will not carry any negative marks.
Papers bearing the code AG, CE, CH, CS, EC, EE, IN, IT, ME, MN, MT, PI, TF will contain questions on Engineering Mathematics to the extent of 20 to 25 marks.
The multiple choice objective test questions can be of the following type:
-
Each choice containing a single stand-alone statement/phrase/data.Example:
Q. The time independent Schrodinger equation of a system represents the conservation of the-
total binding energy of the system -
total potential energy of the system -
total kinetic energy of the system -
total energy of the system
-
-
Each choice containing a combination of option codes.The question may be accompanied by four options P, Q, R, S and the choices may be a combination of these options. The candidate has to choose the right combination as the correct answer.
Example:
Q. The infra-red stretching frequency νco of
(P) Mn(CO)6+ (Q) CO (R) H3B←CO (S) [V(CO)6]- follows the order-
P>R>S>Q -
S>P>R>Q -
Q>S>P>R -
R>Q>P>S
-
-
Assertion[a]/Reason[r] type with the choices stating if [a]/[r] are True/False and/or stating if [r] is correct/incorrect reasoning of [a]Example:
Q. Determine the correctness or otherwise of the following Assertion [a] and the Reason [r]
Assertion: For a fully developedlaminar flow in a circular pipe the average velocity is one half of the maximum velocity.
Reason: The velocity for a fully developed laminar flow in a circular pipe varies linearly in the radial direction.-
Both [a] and [r] are true and [r] is the correct reason for [a] -
Both [a] and [r] are true but [r] is not the correct reason for [a] -
Both [a] and [r] are false -
[a] is true but [r] is false
-
-
Match items: Match all items in Column 1 with correct options from those given in Column 2 and choose the correct set of combinations from the choices A, B, C and D.Example:
Q. Match the following and choose the correct combination
-
Common data based questions: Multiple questions may be linked to a common problem data, passage and the like. Two or three questions can be formed from the given common problem data. Each question is independent and its solution obtainable from the above problem data/passage directly. (Answer of the previous question is not required to solve the next question). Each question under this group will carry two marks.Example:
Common data for Q. 78,79,80: The gas phase reaction, 2P + 4Q → 2R which is first order in P and first order in Q is to be carried out isothermally in a plug flow reactor. The entering volumetric flow rate is 2.5 dm3/min and the feed is equimolar in P and Q. The entering temperature and pressure are 727oC and 10atm respectively. The specific reaction rate at this temperature is 4 dm3/gmol min and the activation energy is 15,000 cal/gmol.
Q.78. What is the volumetric flow rate in dm3/min when the conversion of P is 25%?
(A) 1.88 (B) 5.40 (C) 7.10 (D) 10.80
Q.79. What is the rate of reaction in gmol/(dm3 min) when the conversion of P is 40%
(A) 1.82 x 103 (B) 4.95 x 10-3 (C) 6.2 x 10-3 (D) 9.73 x 103
Q.80. What is the value of the specific reaction rate constant in dm3/gmol min at 1227oC?
(A) 17.68 (B) 22.32 (C) 49.60 (D) 59.75
-
Linked answers question: The question will consist of a problem statement followed by two sub-questions (a) and (b) based on the problem statement. The solution to part (b) depends upon the answer to part (a). Each part (a) as well as (b) in such linked answer questions will carry two marks.Example:
Statement for linked answer Q. 81a & 81b: A reversible Carnot engine operates between the actual heat input temperature of 1000 K and actual heat rejection temperature of 250 K. The ambient temperature is 200 K.
Q.81a The efficiency of this engine will be
A) 5% (B) 20% (C) 25% (D) 75%
Q.81b The above engine is to provide the power output of 100 kW. The heat input required will be
(A) 133.33 kW (B) 400 kW (C) 500 kW (D) 2000 kW
In the above simplistic example, the calculation of heat input in Q.81b requires the value of efficiency calculated in Q.81a as the first step.
-
Structure of the XE/XL Paper Sections-
XE and XL papers contain a number of sections. Each Section is of 50 marks. Each Section will be fully objective type and the questions are divided into three groups.-
Group I: Question Numbers 1 to 10 (10 questions) will carry one mark each. -
Group II: Question numbers 11 to 26 (16 questions) will carry two marks each. -
Group III: Question Numbers 27a to 28b (4 questions) will carry two marks each. Each number in this series (27, 28) will have two subquestions (a & b). The solution to part 'b' will be linked to the correct answer to part 'a', as described above in (e) (vi).
-
-
All questions have four choices with only one being correct. -
Wrong answers carry 25% negative marks in Q1 to Q26 and Q27a, 28a. Marks for correct answers to Q27b, 28b, will be given only if the answer to the corresponding part 'a' is correct. However, Q27b, 28b will not carry any negative marks. -
The types of multiple choice questions are the same as in the Main papers as described above in (e).
-
How to Apply for GATE:
There are two different ways by which candidates can apply for GATE 2006, namely Online Registration and Offline Registration. Detailed information about each of these processes is given below.
Application fee: Rs. 900 for general category and Rs. 400 for SC/ST category.
Online submission ofapplication forms may be made by accessing the websites of IITs and IISc,Bangalore . The candidate should pay the Application Fee through an SBI ATM or through a Demand Draft in favour of ‘IIT Kharagpur’ on any nationalized bank payable at ‘Kharagpur’. The candidate should submit the payment details while filling up the Online Form. Candidates are required to take a print of the Online Application Form after successful submission of data. The printed form, with candidate’s signature and photograph at appropriate places, and the Demand Draft / original ATM transaction-slip must be sent ONLY to The Organising Chairman, GATE, IIT Kharagpur, Kharagpur 721302.
The application fee is not refundable.
Application fee: Rs. 1000 for general category and Rs. 500 for SC/ST category.
Information Brochures and Application Forms are obtainable on payment of cash from the designated Bank Branches corresponding to each zone. The bank pay-in-slip in original must be attached to the candidate’s application during submission. Candidates can also obtain Information Brochures and Application Forms by Post from/or personally at the GATE offices. For this purpose a Demand Draft is to be sent for the amount as above to the Chairman, GATE of the corresponding zonal GATE office, along with a request letter and two self-addressed slips.
Filled in Application Form along with the bank pay-in-slip / receipt of payment from GATE office must be sent to the respective zonal GATE office depending on the examination city where the candidate wishes to appear. -